
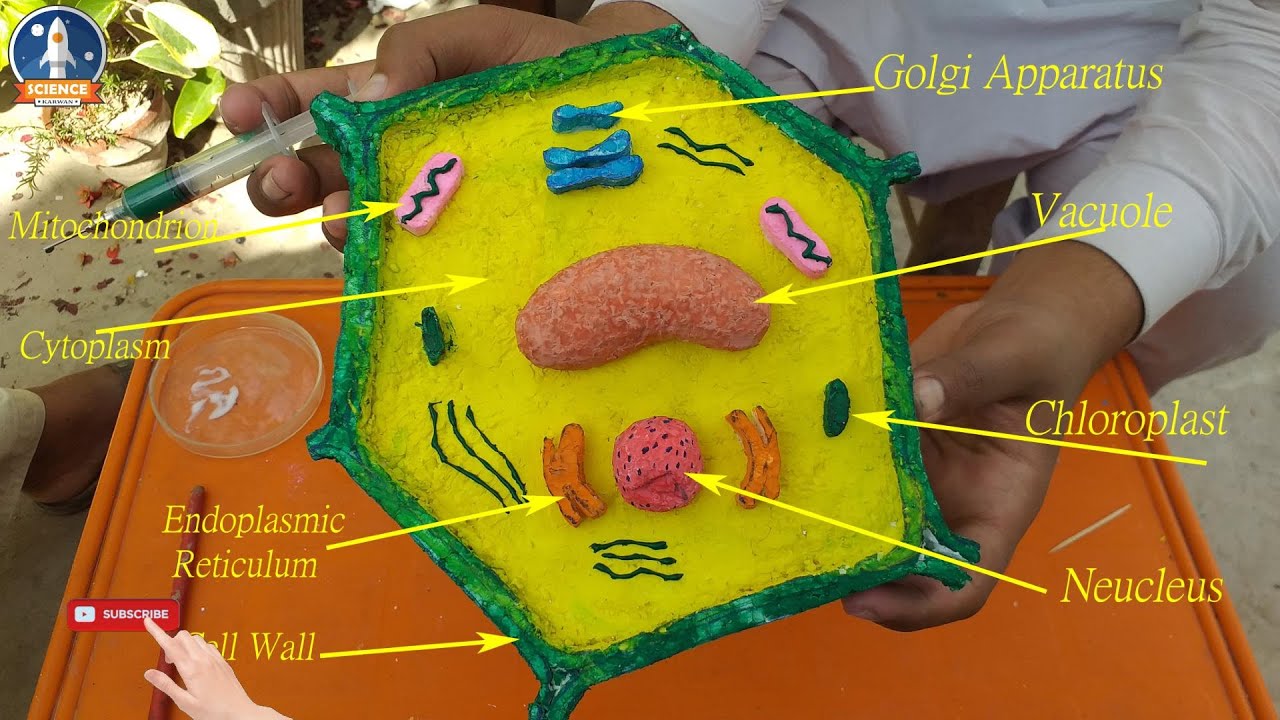
(plural mitochondria): This is the ‘powerhouse’ of the cell. Golgi body: The Golgi body is a stack of membrane-covered sacs that prepares proteins for export from the cell.Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (no ribosomes) The rough endoplasmic reticulum is covered with ribosomes. There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum. The ER helps move proteins within the cell as well as export them outside of the cell. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): The ER is a membrane system of folded sacs and tunnels.They are found in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes: These are little round structures that produce proteins.The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a specialized membrane called the Only eukaryotic cells have nuclei (plural for nucleus), prokaryotic cells do not. It contains Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the genetic material that directs all the activities of the cell. Nucleus NucleusThe nucleus is the ‘control center’ of the cell.Substances such as salts, nutrients, minerals and enzymes (molecules involved in metabolism) are dissolved in the cytoplasm. Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm is a thick, aqueous (water-based) solution in which the organelles are found.It is found just inside the cell wall and is made up of complex lipids (fats) and proteins proteins Cell Membrane: This is a protective layer that surrounds every cell and separates it from its external environment.It makes the cell stiff -providing the cell with mechanical support - and giving it protection. Cell Wall: This is the rigid outermost layer of a plant cell.Plant cell structures (see below for key to numbering) (Source: Let’s Talk Science using an image by jack0m vis iStockphoto). This section will focus on those parts which plants have. A number of these organelles are common to both animal and plant cells. These structures are known as organelles. These include growth and metabolism and reproduction by cell division.Ĭells are made up of subcellular structures that are responsible for different and specific functions. In spite of the differences in size and complexity, all cells are mostly composed of the same substances and they all carry out similar life functions. Animals and plants are examples of eukaryotes (have eukaryotic cells) while bacteria are examples of prokaryotes (have prokaryotic cells). Cells differ in their size and complexity.Įukaryotes are organisms which are made up of large and complex cells, whereas prokaryotes are organisms which are made up of small and simple cells. These organisms are called multicellular (having many cells). While some organisms are single-celled, others are made up of many cells. Please allow extra time for delivery to western states.Cells seen in a plant stem cross-section (Source: RolfDieterMueller via Wikimedia Commons). Additional delivery time may result for some deliveries. * Freight delivery times stated are for average volume items with total order weight under 5kg for metro areas in eastern states. Freight will be charged at checkout for these items. Same/Next day: 0 - 2 working days** Delivery Chargesįree delivery exclusions apply to some bulky and large items. Standard/Road Freight: 2 - 5 working days* Your order can be delivered to anywhere throughout mainland Australia by standard (road) freight delivery.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
